IDŐJÁRÁS - angol nyelvű folyóirat
Vol. 128, No. 2 * Pages 143–286 * April - June 2024
 letöltés [pdf: 22872 KB]
letöltés [pdf: 22872 KB]
Analysis of daily and hourly precipitation interpolation supplemented with radar background: Insights from case studies
Kinga Bokros, Beatrix Izsák, and Zita Bihari
DOI:10.28974/idojaras.2024.2.8 (pp. 267–286)
Kinga Bokros, Beatrix Izsák, and Zita Bihari
DOI:10.28974/idojaras.2024.2.8 (pp. 267–286)
IDŐJÁRÁS folyóirat
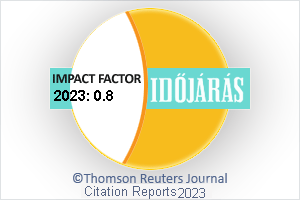
Az IDŐJÁRÁS a HungaroMet Nonprofit Zrt. negyedévenként megjelenő angol nyelvű folyóirata
Megrendelhető a journal.idojaras@met.hu címen.
A szerzőknek szánt útmutató itt olvasható.
Megrendelhető a journal.idojaras@met.hu címen.
A szerzőknek szánt útmutató itt olvasható.










